Fintech has numerous growth areas, and blockchain technology has recently become a popular topic. If you've heard about blockchain but need clarification, you've come to the right place!

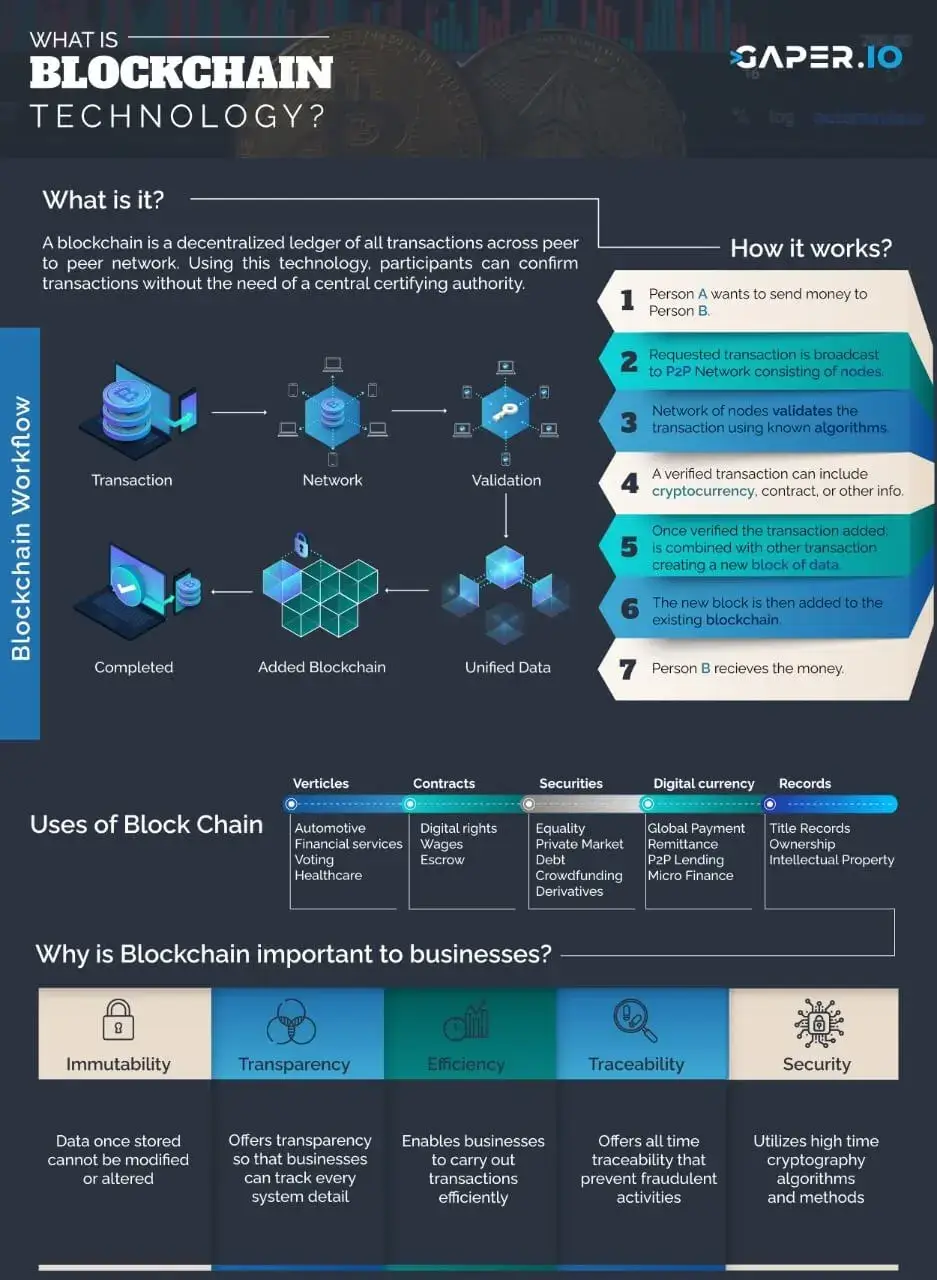
Blockchain is a method of storing data. Its data is built in such a manner that is difficult or impossible to alter, hack, or defraud. Moreover, it is a digital log of transactions. This log distributes throughout the complete network of computer systems.
A blockchain organizes data into groupings called blocks. Each of which contains a collection of data. Blocks have specific storage capabilities. When they are full, they are closed and connected to the preceding block. It produces a data chain known as the blockchain.
Why is blockchain technology generating so much buzz? The major reason behind it is the popularity of its Security Feature. In numerous ways, the technology delivers decentralized security and trust. For starters, new blocks are always recorded in a linear and chronological order.
Information is the lifeblood of business. The sooner, the more precise it receives, the better. Orders, payments, accounts, production can be tracked via a blockchain network therefore, you can see all facts of a transaction end-to-end. Since members share a single view of the truth, it provides you more confidence.
A chain of blocks that contain information. That’s it? Not quite. It was created in 1991 to be used as digital time stamps. Yet, never became into anything big, until Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2009.
It is a sort of distributed ledger technology. In this tech, all transactions are recorded one by one. Moreover, it is also using an immutable cryptographic signature known as a hash.
However, this implies that if a single block in a chain is modified, it will be immediately clear that the chain has been tampered with. Thus, hackers would have to modify every block in the chain across all distributed copies of the chain, if hey intended to destroy a blockchain system.
The technology is a hybrid of three cutting-edge technologies: First, keys used in cryptography. Second, a peer-to-peer network with a distributed ledger. Third, a computer system for storing network transactions.
Each block has 3 things inside:
A hash digit is a long chain of alphanumeric characters that are unique to that block. For example, a URL that is only valid for one website. This hash is almost impossible to change. If something inside the block has changed, it alters the hash as well.
This indicates the formation of a new block which can then linked to the previous block. By having the hash of the previous block and its own, a block can create a chain of blocks.
This is where security is maximum. So, if one thing changes, it leads to the creation of another block and you can track when that changed. Therefore, all changes recorded and seen by others.
The following are the four basic principles underpinning:
Ledger: It is a shareable form. A shared ledger is a distributed system of record. Across a corporate network, this ledger shared and is “append-only.”
Permissions: Transactions are safe, authenticated, and verifiable, all thanks to permissions.
Smart contracts: Smart contract is a contract or set of rules. It governs a commercial transaction.
Consensus: All parties agree to the network-verified transaction by consensus.
“Proof-of-work” is a concept in the blockchain when producing new blocks. This mechanism slows the process of creating new blocks to around 10-15 minutes. Although this seems like a very slow process.
It is useful because if someone wants to hack into this system, it will take many minutes to alter the data in one block. Yet, you can’t just alter the data for one block, because it’s a blockchain. Thus, it’ll take them a considerable amount of time to change the data in all the blocks in the chain which would prevent such things from happening.
A question that comes to mind is, well who manages blockchain? Who says it is correct or not? Who is the main authority behind this chain? The answer to all these questions are, everyone! In a blockchain, power is all over the structure. Even shared among everyone who joins the block.
So, for instance, if you are sending money to a few friends, all of your friends will share the blockchain and everyone can see it. When a new block gets into its real formation then it needs its hash digits to match the ones in the blockchain that everyone has. If it does, then it becomes a part of the blockchain. If it doesn’t, it has to reject and does not become a part of the blockchain.
Through this method, blockchains are monitored and governed by everyone using them. Thus, it also adds another layer of security when people are dealing with sensitive and important data.
There are four distinct types of blockchains. The following are the details:
Networks of Private Blockchains: It works well for private corporations and organizations since it operates on closed networks.
Blockchain Networks in the Public Sector: Certain obstacles and issues, such as security weaknesses and centralization, can be addressed with its assistance.
Blockchain Networks with Permissions: Permissioned blockchain networks, also known as hybrid blockchains. They are private blockchains that grant privileged access to approved persons.
Blockchains in a Consortium: Permissioned blockchains are similar. Although these blockchains are more difficult to set up at first. Once they are up and running, they can provide more security.

Matchpool: It is a successful matchmaker in a variety of fields. It forms dating to freelancing to Uber and Airbnb.
Block point: This makes it easier to create payment systems.
Loyal: It is a blockchain-based smart contract platform.
Bitcar: A BitCar token allows for fractionalized ownership of collectible autos.
IBM Blockchain: It is vital to understand the status and quality of every product. Even in your supply chain, from raw materials to distribution.
Proof of Insurance: It aids law enforcement in verifying insurance in real-time.
Food Industry: Blockchain can increase the transparency and efficiency of determining. Whether foods are tainted or they are contaminated across the supply chain.
Blockchain can be used in many places around the world. Some are more famous than others, such as Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. People can send money to each other without an intermediary like a bank.
Just like this, it is also used in the supply chain. Where firms need to make sure when certain perishable items were produced. As blockchains cannot be further altered, one can know exactly when something is produced, delivered, or received.
More Trust: With this feature, only network users can use the blockchain. Who has expressly allowed access will have access to the records?
Superior Security: A transaction cannot be deleted by anybody. Even the system administrator cannot delete or remove it.
Supplementary Efficiencies: It is a set of rules known as a smart contract. It is placed on the blockchain and implemented automatically to speed up transactions.
What does blockchain mean in cryptocurrency: Is there a difference between blockchain and cryptocurrency? Blockchain is the technology that allows cryptocurrencies to exist. The most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin. It is the one for which blockchain technology was in-actual created.
What does blockchain mean for business: The technology enables the safe exchange of corporate operations. Contracts, corporate records, and other documents are sent between organizations and partners. They are in encrypted form and this effectively produces a detailed record of all corporate transactions, events, and aspects.
What does blockchain mean for banks: It can hold information such as who owns a certain piece of property or a bond. The technology is used to retain an immutable record of ownership. It facilitates asset transactions between parties that are distrustful of one other.
Gaper.io is releasing its deep dive into Fintech with more analysis and explanations. Stay tuned for more articles in the coming weeks.
Top quality ensured or we work for free
